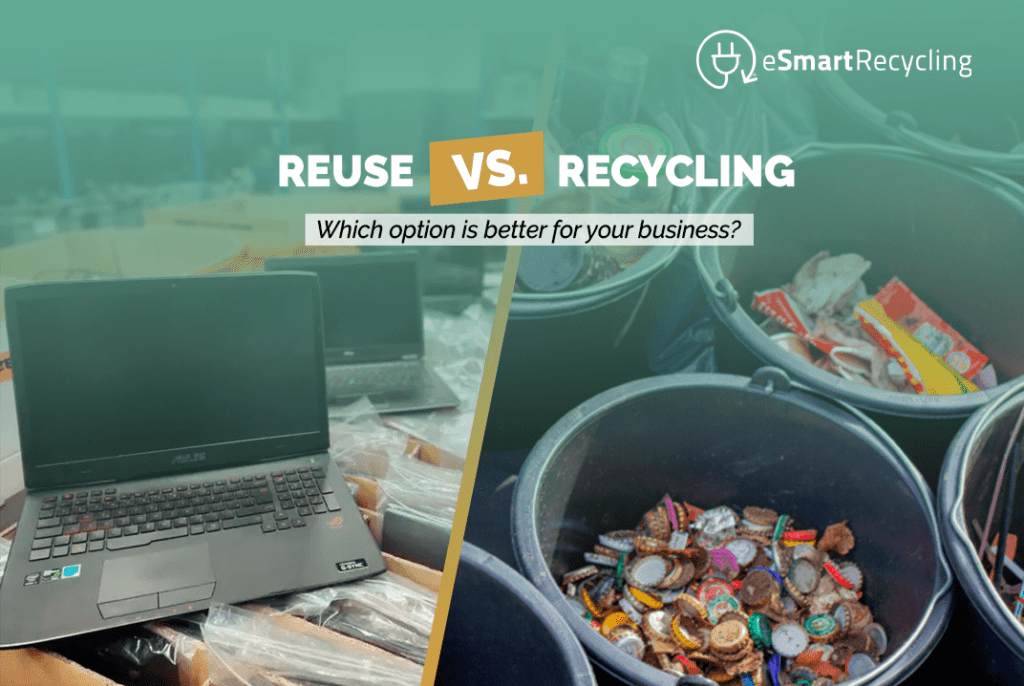
As businesses become more aware of their environmental impact, they take recycling and material reuse more seriously. Both strategies to reduce waste and carbon footprint have their pros and cons. So, should your business focus on reusing materials or working to recycle them? This article will analyze reuse versus recycling to determine which option is better for your business.
Reuse involves using something again, either in its original state or adapted for a different use. This practice can reduce the amount of waste a company produces and save money at the same time. Reuse can involve things like office supplies, clothing, electronics, and construction materials. Some companies even seek out items that others have discarded, which is how businesses like Goodwill and The Salvation Army make money.
Recycling is the process of reprocessing old and used materials to make new products. It reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and decreases the use of raw materials to create new products. Commonly recycled materials include paper, glass, aluminum, metal, and plastic. Some modern companies have even started recycling organic materials, like wood waste and food scraps.
The primary benefit of reuse is that it reduces the amount of materials a company throws away and can save money. Additionally, many businesses look for new and innovative ways to reuse items that others might have discarded, keeping them out of landfills and saving resources. However, the downside of reuse is that it can be time-consuming for businesses to find new uses for old items. The quality of reused items can sometimes be inferior to new ones, and it can be challenging to find genuinely reusable items, as some may need repairs or upgrades to be reused.
The biggest benefit of recycling is that it reduces the amount of waste going to landfills, saving valuable space. Recycling also helps conserve natural resources and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. However, the drawbacks of recycling include the high energy consumption required for transportation and processing. Additionally, not all items are recyclable, and the quality of some recycled materials can be inferior to non-recycled materials.
Deciding whether a business should focus on reuse or recycling can be a tough decision. However, in most cases, the best approach for a business is to do both. Companies should consider the materials they have and whether they can be reused or recycled. Many businesses also choose to focus on reusing items that cannot be recycled and recycling those that can. By using both reuse and recycling, companies can significantly reduce their environmental impact and save resources at the same time.
Both reuse and recycling are strategies for businesses to reduce waste and conserve resources. Each option has its pros and cons, but in most cases, companies should focus on both. Reusing items can help save money and reduce waste, while recycling can help conserve resources and reduce landfill waste. By utilizing both strategies, businesses can have a positive impact on the environment and save money in the process.
Fill out the form below to request your electronics recycling pickup.
We’ll coordinate the schedule logistics and follow up with next steps.
Businesses replace computers regularly, but recycling often gets postponed. Devices end up stored in closets, warehouses, or unused rooms with no clear plan. Over time, that pile grows and becomes harder to manage.
Knowing where to recycle computers in Tampa Bay helps close that process in an organized and secure way that aligns with internal company policies. It’s not just about getting rid of equipment, but about handling it correctly.
Business computers are not ordinary waste. They store internal information, system access credentials, emails, and, in many cases, customer data. When devices sit unused without control, the risk doesn’t disappear; it just gets delayed.
There’s also an operational side to consider. Storage space gets taken up, asset inventories become inaccurate, and IT teams lose visibility over what equipment still exists. That’s why choosing the right computer recycling Tampa Bay option is an operational decision, not just a logistical one.
Tampa Bay offers several alternatives for computer recycling, but they don’t all serve the same needs.
Municipal recycling centers often accept certain electronics, but they usually don’t provide data destruction services or detailed documentation. For businesses, that level of service is often not enough.
Community collection events can be useful, but they tend to be occasional and limited in volume. They work for one-time situations, not for ongoing business needs.
Companies that specialize in electronics recycling in Tampa Bay operate differently. They focus on business volumes, scheduled pickups, data handling, and reporting, which are key factors for organizations that need structure and accountability.
Recycling computers at a company level involves more than dropping off equipment. A reliable option should include equipment pickup, controlled handling, and secure data destruction.
Documentation is another essential piece. Businesses often need records for internal audits, compliance reviews, or partner requirements. Without proper documentation, the recycling process remains incomplete.
One common mistake is assuming that deleting files or resetting a computer is enough. In business environments, that approach falls short.
The Federal Trade Commission advises specific practices for disposing of electronics that contain sensitive information, warning that improper disposal can lead to data exposure and legal issues. The FTC guidance can be found here:
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/disposal-old-electronics-what-you-need-know
When evaluating where to recycle computers in Tampa Bay, data destruction should be one of the main criteria.
Some local options work well for a small number of devices, but recycling dozens or hundreds of computers requires a different setup.
In these cases, working with computer recycling services Tampa Bay that can handle volume, scheduling, and on-site pickup helps avoid operational disruption. Planning makes the process smoother for IT and operations teams.
Not every retired computer is unusable. Some devices can be reused or refurbished, depending on their condition.
Certain recycling providers evaluate incoming equipment and, when appropriate, redirect it toward reuse or donation programs. For many businesses, knowing that part of their technology continues to be useful adds value to the recycling decision.
Another key factor is visibility after the equipment leaves the office. Businesses need to know what happened to their devices.
Recycling reports provide clarity on how equipment was handled and help maintain clean internal records. Without traceability, companies lose oversight of their retired technology.
Choosing a local provider makes coordination easier. In Tampa Bay, working with a company that understands the needs of regional businesses simplifies communication and scheduling.
We, at eSmart Recycling, work with Tampa Bay businesses to manage out-of-use computers in a secure, organized, and documented way. We support companies from planning through process completion.
Knowing where to recycle computers in Tampa Bay is about more than finding a nearby location. It’s about selecting an option that supports security, organization, and internal policies.
When recycling is handled clearly and on a regular basis, computers stop being a stored problem and become part of a controlled process. For businesses, that means fewer risks and better control over their technology lifecycle.
One of the most common questions businesses ask is not if they should recycle their computers, but when. Many companies keep older devices out of habit, store them “just in case,” or replace them without a clear plan for what comes next. Understanding how often businesses recycle computers helps bring order to technology decisions, reduce risk, and avoid unnecessary stockpiling.
There isn’t a single rule that works for every company. The right timing depends on how the equipment is used, the type of data it holds, and internal IT policies.
In most organizations, desktop computers and laptops have an average business lifecycle of three to five years. This range is commonly referenced in corporate IT planning and manufacturer guidance. After that period, devices often begin to show slower performance, compatibility issues with updated software, and increased security risks.
At that stage, many companies replace the equipment but delay recycling it. Recycling at the right time prevents unused computers from sitting in storage with no clear control or visibility.
Beyond age, there are practical signals that indicate when companies should recycle old computers. One of the most important is the end of manufacturer support or security updates for the operating system. Devices without updates are more vulnerable to known threats.
Another sign is rising maintenance time and cost. When keeping a device running takes more effort than replacing it, holding onto it no longer makes operational sense. Performance limitations that interfere with basic job tasks are also a clear indicator.
Storing unused computers may seem harmless, but it creates real risks. Data security is the biggest concern. A stored device can still contain sensitive information such as emails, credentials, internal files, or customer data.
The Federal Trade Commission warns that improper disposal of electronics with stored data can lead to security incidents and regulatory issues. The FTC provides guidance on safe electronics disposal here:
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/disposal-old-electronics-what-you-need-know
Beyond data, unused technology takes up physical space, complicates asset tracking, and often leads to uncertainty about what equipment is still active.
Not all businesses use technology in the same way. Administrative offices with stable workloads often keep devices closer to the upper end of the lifecycle range. Companies in design, engineering, or software development usually replace and recycle computers more frequently due to higher performance demands.
Organizations that handle sensitive information, such as healthcare or financial data, often follow shorter timelines. In these cases, the decision is driven as much by security as by performance. Establishing a business computer recycling schedule helps avoid last-minute or inconsistent decisions.
A common pattern is replacing computers while keeping the old ones in storage. Over time, these devices become outdated, unmanaged, and easy to forget. This creates two problems: no one knows exactly how many devices exist or what data they contain, and when recycling finally happens, the volume is harder to manage.
Regular recycling prevents these buildups and keeps technology inventories under control.
Many companies already have policies for purchasing and replacing equipment, but recycling is often missing from that process. Including recycling from the start helps close the loop.
When IT teams plan for electronic recycling for businesses alongside replacements, device tracking improves, and the administrative burden decreases. This also supports audits and internal reviews.
When computers are retired, related equipment should be reviewed as well. Monitors, keyboards, mice, docks, cables, and accessories are frequently overlooked, even though they also require proper handling.
A complete recycling process considers the full workstation, not just the main device.
A frequent question is when companies replace and recycle computers. In many cases, both actions happen together, but timing can vary. Some businesses recycle immediately, while others wait for accounting cycles or project milestones.
What matters is setting a clear maximum timeframe between replacement and recycling so devices are not forgotten.
Partnering with a specialized provider simplifies the process. At eSmart Recycling, we help businesses decide when to recycle, which equipment to include, and how to manage data securely.
This support turns recycling into a routine part of operations rather than a lingering task.
Knowing when to recycle computers is about more than device age. It’s about security, organization, and clear internal processes. Companies that define timelines and procedures avoid accumulation, reduce risk, and keep their technology under control.
If your business has already replaced equipment or is planning to do so, reviewing what devices are still stored is a strong first step. Recycling at the right time keeps IT operations cleaner and prevents future issues.
Businesses in Tampa deal with technology turnover all the time. Computers get replaced, monitors stop being used, servers are upgraded, and boxes of cables start piling up in storage rooms. The questions usually come together: what can we recycle, how do we handle it properly, and what happens to the data.
We work with those questions every day. That’s why we offer electronic recycling services for businesses in Tampa designed to be clear, secure, and easy to manage. From the first pickup to the final report, we make sure companies know exactly what happens with their equipment.
One of the first challenges companies face is logistics. Moving large volumes of equipment takes time, planning, and staff availability that many teams don’t have.
We coordinate electronics pickup for businesses in Tampa directly from offices, warehouses, or data centers. This includes desktop computers, laptops, monitors, printers, servers, networking equipment, cables, and accessories. Pickups are scheduled around each company’s operations so daily work is not disrupted.
Every collection is documented from the start, which helps keep internal records organized and avoids confusion later on.
For most businesses, data security is the main concern. Data does not disappear when a device is no longer in use.
We provide secure data destruction services that follow recognized standards in the United States and align with requirements such as HIPAA when applicable. Each device goes through a documented process to make sure stored information is permanently removed.
After the process is complete, companies receive certificates of data destruction, which are often required for audits, internal compliance, and security policies.
Not all equipment can be reused, but all of it needs to be handled responsibly. We manage electronic recycling for businesses with processes that prevent materials from ending up in landfills.
Devices that cannot continue in use are dismantled and processed according to their components. Metals, plastics, and other materials are routed through proper recycling channels within the electronics recycling industry.
This is especially relevant for companies that track environmental practices or need documentation for internal or external reporting.
Some of the equipment we receive is still functional or can be repaired. When that’s the case, we refurbish those devices and direct them toward donation programs.
A portion of our revenue is allocated to repairing and donating technology to communities with limited access to devices. For many businesses, this adds an extra layer of value, knowing that part of their retired equipment continues to be useful to others.
This reuse activity is tracked and can be reflected in the reports we provide.
Electronic recycling does not end when the equipment leaves the office. Many organizations need clear documentation to support internal processes.
We provide detailed recycling reports that show what types of devices were handled, how many were reused, how many were recycled, and how data was managed. These reports help IT, procurement, legal, and sustainability teams keep accurate records.
They also make it easier to respond to partner requests, internal reviews, or compliance checks.
A common question we hear is what electronics businesses recycle in Tampa. In most cases, companies recycle:
Computers and laptops, monitors and displays, printers and scanners, servers and networking equipment, keyboards, mice, cables, and accessories.
If there is uncertainty about a specific device, we review it before scheduling the pickup to avoid surprises.
Choosing an electronic recycling company for businesses in Tampa is not just an operational decision. It also relates to security, organization, and accountability.
Centralizing technology recycling helps prevent common issues such as forgotten equipment, unmanaged data, or improper disposal. It also frees up physical space and reduces internal tasks that often get delayed.
We work alongside companies as an operational partner, helping them keep technology management under control instead of adding complexity.
The process usually begins with a simple conversation. We review the types of equipment a company has, estimated volumes, and any specific requirements related to data or reporting.
From there, we outline a plan that includes pickup, data handling, recycling, and documentation. Everything is scheduled with clear timelines so teams know what to expect at each step.
Managing retired technology does not need to become a recurring headache for IT or operations teams. When electronic recycling is handled with clear steps, secure data destruction, and proper documentation, it becomes another organized part of doing business.
We work with companies across Tampa to handle electronics responsibly, keep data protected, and provide visibility into what happens after devices leave the office. If your business is ready to clear out unused equipment and handle it the right way, we’re ready to help.
Recycling old laptops without risking your data is possible, but only when the process is handled correctly. For businesses, outdated laptops often contain years of emails, credentials, internal files, and access to cloud systems. Even when devices are no longer in use, the information stored on them can still be recovered if they are handled improperly.
The key is understanding what needs to happen before a laptop leaves your control and choosing a recycling path that addresses data responsibility from start to finish.
Many businesses assume that deleting files or performing a factory reset is enough before recycling a laptop. In reality, those steps often leave recoverable information behind. Storage devices can retain data fragments, user profiles, and system records that are not visible to the average user.
For companies managing employee devices, this becomes a serious concern. Laptops may include personal data, client information, financial records, or credentials that grant access to internal systems. Once a device leaves the office without proper handling, the company remains responsible for what happens to that data.
This is why recycling laptops should never be treated as a basic disposal task.
Before a laptop can move into any recycling stream, its data must be addressed in a controlled way. This step determines whether the device can be reused or must be dismantled.
Responsible recycling starts with identifying storage components and deciding how they will be handled. In some cases, data can be permanently removed so the laptop can be reused. In others, storage devices need to be physically destroyed to eliminate recovery risk.
What matters most for businesses is having certainty that data cannot be accessed again and that the process is documented.
At eSmart Recycling, we work specifically with old and outdated laptops from businesses, offices, and organizations. We receive devices that are no longer in use, assess their condition, and determine the safest path forward for each one.
We handle laptops that can still be reused as well as those that are no longer functional. In both cases, data is addressed before anything else happens. Laptops do not move forward in the process until storage components are handled under controlled conditions and recorded.
Our goal is simple. Old laptops leave our facility without data and without unanswered questions for the company that trusted us with them.
Not every old laptop needs to be destroyed. Many devices can be reused if they are still functional and meet certain criteria. Reuse can include internal redeployment, resale through approved channels, or donation through structured programs.
However, reuse only works when data has been fully addressed first. Without proper controls, reuse becomes a liability rather than a benefit.
The Environmental Protection Agency encourages the reuse of electronics when devices are handled responsibly and data risks are managed correctly.
For businesses, reuse should always be paired with records that confirm how data was handled before the laptop changed hands.
Older or damaged laptops are often not suitable for reuse. In these cases, devices are dismantled so materials can be recovered.
During dismantling, laptops are separated into components such as metals, plastics, batteries, and circuit boards. Storage devices are removed and handled separately to ensure data risks are eliminated. Materials are then sent to specialized processors that handle them according to environmental and safety requirements.
This stage requires oversight. Without tracking and downstream controls, laptops can end up in informal channels that expose businesses to unnecessary risk.
Not all recycling services follow the same rules. Certification plays a key role in determining how laptops and their data are handled.
R2v3 is one of the most widely recognized standards in the electronics recycling industry in the United States. It is managed by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International and defines requirements for data handling, environmental practices, worker safety, and downstream accountability.
Under R2v3-certified operations, recyclers must document how devices are processed and where materials are sent. These requirements are reviewed through independent audits.
We operate under R2v3 certification because businesses need confirmation that old laptops are recycled under verified processes, not assumptions.
https://sustainableelectronics.org/r2v3/
A secure laptop recycling process does not end when devices are collected. Businesses should expect documentation that supports what was done.
This includes inventory records, confirmation that data was addressed, and reports showing whether laptops were reused or dismantled. These documents support internal audits, compliance reviews, and sustainability reporting.
Without this information, recycling becomes a blind spot.
We work with businesses that want old laptops removed responsibly and permanently. At eSmart Recycling, we recycle outdated laptops under controlled, R2v3-certified processes and provide documentation that closes the loop.
For companies, recycling laptops should reduce risk, not create new concerns. Devices are handled properly, data is addressed before anything else, and records are delivered at the end. That clarity is why many organizations trust us to recycle their old laptops safely.
Companies in Florida have several options when it comes to recycling electronic equipment. However, not all options offer the same level of control, documentation, or assurance once devices leave the office. For businesses, the real challenge is not finding an option but choosing one that fully aligns with their responsibilities around data, compliance, and accountability.
Understanding how these options differ helps companies make informed decisions and avoid risks that often appear after electronics are already out of sight.
One of the most reliable options for companies in Florida is working with a certified electronics recycling provider that specializes in commercial equipment. These providers handle office electronics such as computers, servers, networking devices, printers, and accessories through structured processes.
Certified recyclers operate under defined standards that govern how equipment is received, processed, and documented. This option is commonly chosen by businesses that require traceability and clear records for internal or external reviews.
At eSmart Recycling, we work with companies that need this level of structure. Devices are inventoried, processed under controlled conditions, and supported by documentation that closes the loop properly.
Some companies prefer on-site recycling services, especially when handling large volumes of equipment or devices tied to sensitive operations. With this option, certain steps, such as inventory verification or physical destruction of storage components, are performed at the company’s location.
On-site services provide added visibility and reduce handling risks during transportation. They are often used by organizations with strict internal policies or heightened data concerns.
While not required for every project, on-site services can be a practical option when companies need direct oversight during the early stages of the process.
Another common option for Florida businesses is scheduled pickup followed by centralized processing at the recycler’s facility. This approach is well-suited for companies with routine equipment refresh cycles or multiple office locations.
After pickup, electronics are transported securely and processed at facilities designed for sorting, testing, dismantling, and material recovery. When managed properly, this option balances convenience with accountability.
The key factor is what happens after processing. Without reporting and downstream transparency, businesses lose visibility into the final destination of their equipment.
Some manufacturers and IT vendors offer take-back programs for their products. These programs usually apply to specific brands or device models and may require advanced coordination.
While take-back programs can be useful in limited cases, they often provide minimal insight into how electronics are handled after return. Documentation related to data handling or material recovery may also be limited.
For this reason, many companies treat take-back programs as a partial solution rather than a complete recycling strategy.
Donation is another option available to companies in Florida, particularly for equipment that still functions and meets reuse criteria. Donated electronics can support schools, nonprofits, or community initiatives when handled responsibly.
Before donation, devices must be evaluated, and data must be fully addressed. Without proper controls, donations can expose businesses to data risks and compliance issues.
The Environmental Protection Agency encourages reuse and donation when electronics are handled safely and responsibly.
For companies, donation works best when paired with a recycling partner that manages data handling and provides documentation.
Not all electronics are suitable for reuse or donation. Older or damaged equipment is typically dismantled so materials can be recovered.
During this process, devices are separated into metals, plastics, circuit boards, and other components. These materials are sent to specialized processors that handle them under environmental and safety regulations.
Where materials go depends on how well downstream partners are managed. This is one of the areas where standards and audits play a critical role.
One of the clearest ways to evaluate recycling options is through certification. The R2v3 standard, managed by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International, defines how electronics, data, and materials must be handled.
R2v3-certified recyclers are required to document processes, track downstream vendors, and undergo independent audits. This provides businesses with verification rather than assumptions.
We operate under R2v3 certification because it gives companies confidence that their electronics are handled properly from start to finish.
https://sustainableelectronics.org/r2v3/
Many companies in Florida explore several electronics recycling options before deciding. Pickup services, donation programs, take-back options, and certified recyclers may all appear viable at first glance.
What usually drives the final decision is visibility. Businesses want to know what happens to their electronics, how data is handled, and what documentation they will receive. When those answers are unclear, the option quickly loses value.
This is why many companies move away from fragmented solutions and look for a single partner that can manage the entire process with accountability.
At eSmart Recycling, we work with companies that want one clear electronics recycling solution in Florida. We manage the full process, from inventory and data handling to processing and final reporting, under R2v3-certified operations.
Rather than offering partial services, we provide a structured path. Companies know where their electronics go, how they are handled, and receive documentation that supports audits, compliance reviews, and internal reporting.
For businesses in Florida, choosing eSmart Recycling means removing uncertainty from electronics recycling. Devices are handled responsibly, data risks are addressed properly, and the process closes with clear records. That consistency is why many companies see us not just as a recycler, but as their long-term electronics recycling partner.
Recycled office computers in the United States do not all share the same destination. Some are reused, others are dismantled for materials, and a portion is destroyed under controlled processes. What determines where these devices end up is not only their condition, but how the recycling process is managed from the start.
For businesses, knowing where office computers go after recycling matters. It impacts data security, regulatory compliance, and the management of technology assets once they leave the workplace.
The recycling process begins with identification and tracking. Before any technical work takes place, each computer is reviewed, logged, and associated with an inventory record. This step allows businesses to maintain visibility over devices that once stored internal data.
Responsible recyclers treat this phase as a control point. Without proper inventory, computers can move through informal channels, increasing the risk of data exposure or loss of accountability.
When we receive office computers, every unit is documented before it moves forward.
Office computers often store years of internal information. Emails, user credentials, financial files, and access tokens can remain on devices long after they stop being used.
Because of this, no computer should be reused or processed before its data is fully addressed. Storage media is handled based on device condition and reuse criteria. In some cases, data is permanently removed so the device can be reused. In others, storage components are physically destroyed.
What matters for businesses is not the technical method, but the assurance that data cannot be recovered and that the process is documented.
This step is what separates responsible recycling from basic disposal.
A portion of recycled office computers in the US is suitable for reuse. Devices that pass inspection and data handling requirements may be refurbished and returned to service through controlled channels.
Reuse can take several forms. Some computers are redeployed internally by organizations. Others enter secondary markets or structured donation programs. In all cases, reuse only happens after data has been fully addressed.
The Environmental Protection Agency confirms that reuse reduces demand for raw materials and extends the useful life of electronics.
For businesses, reuse works when downstream partners are known and properly managed.
Not every office computer qualifies for reuse. Older models, damaged units, or devices with outdated components are usually dismantled.
During dismantling, computers are separated into material categories. Metals, plastics, circuit boards, and glass are processed by specialized facilities. Valuable materials such as copper and precious metals are recovered, while hazardous substances are handled under environmental controls.
This stage is where transparency becomes critical. Without oversight, materials can be mismanaged or exported without proper safeguards.
One common question businesses ask is whether recycled computers stay in the US or are sent overseas.
Export of electronic waste is regulated and closely monitored when handled correctly. Issues arise when recycling lacks oversight or when downstream vendors are not properly vetted.
International agreements like the Basel Convention highlight the risks associated with uncontrolled electronic waste movement.
Certified recyclers are required to document downstream partners and ensure materials are processed in approved facilities, whether domestic or international.
R2v3 certification plays a central role in determining the final destination of recycled office computers. The standard is managed by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International and applies strict requirements to data handling, material processing, and downstream accountability.
Under R2v3-certified operations, recyclers must prove where equipment goes, how materials are handled, and how data risks are controlled. These requirements are verified through independent audits.
We operate under R2v3 certification because businesses need clarity, not assumptions, about what happens after recycling.
More information about the standard is available here:
https://sustainableelectronics.org/r2v3/
For businesses, the final destination of office computers should never be a mystery. Proper recycling includes documentation that supports every step of the process.
This usually includes asset inventories, confirmation of data handling, and recycling or processing reports. These records support internal audits, sustainability reporting, and compliance reviews.
We make sure that businesses receive clear documentation showing what happened to each device.
No. Reuse depends on condition, age, and handling requirements. Many devices are dismantled instead.
Properly recycled computers should not. Certified processes direct materials to approved processors.
Yes. Tracking is possible when recyclers provide downstream transparency and reporting.
Yes. Certification defines how devices are processed and where materials are allowed to go.
Where office computers end up after recycling is not a technical detail. It is a business decision that affects data responsibility, reporting, and trust. Once devices leave the office, the company is still accountable for what happens next.
Businesses that understand this do not look for the fastest exit for old equipment. They look for clarity. They want to know whether computers are reused, dismantled, or processed as materials, and they want records that support those outcomes.
Working with an R2v3-certified recycler provides that clarity. It establishes rules, traceability, and verification across the entire process. There are no assumptions, no loose ends, and no unanswered questions.
For us, recycling office computers is about closing the loop properly. Devices leave the workplace, but responsibility does not disappear with them. A clear process, backed by certification, is what ensures that old office computers end up exactly where they should.






Did you enjoy our latest blog articles just above?
Subscribe to receive new stories, insights, and impact updates straight to your inbox.
We’ll send you curated content about our partners, recycling strategies, success stories, and how your involvement is driving change through technology access and digital empowerment.
💡 No spam, just the smart stuff.