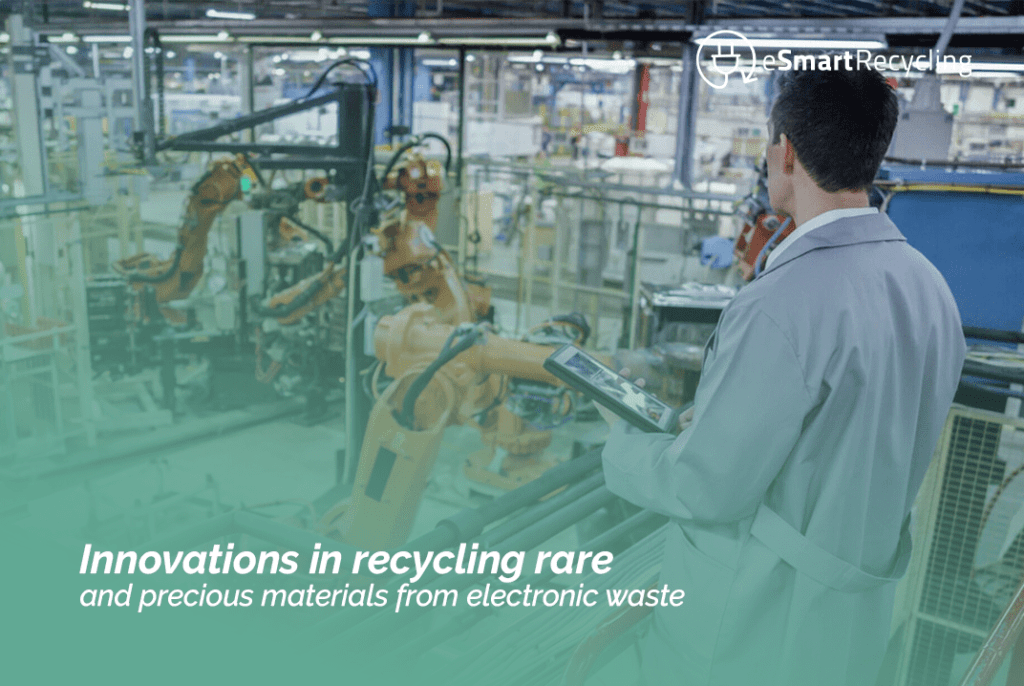
With the exponential growth of electronic waste (e-waste) worldwide, it is increasingly necessary to recycle and reuse valuable materials and components from devices. Advanced recycling technologies are now emerging to help reduce the environmental impact of electronic waste and maximize the reuse of rare and precious materials for future devices. This article examines recent innovations in e-waste recycling, the potential benefits for the environment and economy, and highlights some solutions the world can benefit from.
Electronic waste is one of the fastest-growing waste streams globally, already exceeding 50 million metric tons per year. At the current growth rate, e-waste levels are projected to triple by 2050. This waste contains valuable rare and precious elements such as platinum, gold, and palladium, but also many hazardous elements like mercury, lead, and arsenic. Currently, the recycling of these valuable materials is inadequate, resulting in large quantities of useful materials being wasted, while increasing amounts of hazardous materials end up in landfills, damaging the environment and potentially threatening human health. Therefore, innovative technologies are needed to recycle e-waste, new approaches to prevent environmental harm, and measures to maximize the reuse of valuable materials.
Recent advances in e-waste recycling include the development of new processes and technologies that can effectively recover rare, precious, and valuable materials. One example is microfactory systems, designed to process e-waste on-site and efficiently recover valuable materials from discarded devices. These microfactory systems utilize emerging technologies such as nanotechnology, biotechnology, and robotics to recover valuable materials and device components from e-waste.
This approach reduces the need for large, energy-consuming recycling plants and decentralizes recycling capacity, making it easier for local communities to manage their e-waste in a socially, economically, and environmentally sustainable manner.
Other advancements in e-waste recycling include the development of innovative and efficient methods for recovering rare and valuable metals and materials. These recovery methods often use novel solvents, chemical treatments, and biotechnological processes to effectively recover and purify rare and valuable metals.
Examples of recovery technologies include supercritical fluid extraction processes, ionic liquids, and bioleaching processes. To maximize the benefits of these recovery technologies, it is also important to develop and implement recycling policies and regulations that promote the recycling of rare and valuable materials and chemicals.
E-waste recycling offers many potential benefits for the environment, economy, and society. Recycling e-waste can help reduce the environmental impact of electronic products by diverting valuable and hazardous materials from landfills and dumpsites. This can reduce air and water pollution and help preserve wildlife habitats and ecosystems.
E-waste recycling also has the potential to create new jobs and opportunities for local communities, as new microfactory systems can be established to recycle e-waste in a socially, economically, and environmentally sustainable manner. Additionally, recovering rare and valuable materials from e-waste can help reduce the import and export of raw materials and, therefore, reduce the negative impact of raw material extraction and processing on the environment and society.
Several leading brands are developing and implementing innovative e-waste recycling technologies, processes, and solutions. For example, Apple has also introduced its e-waste recycling process, called “Apple Reuse and Recycling Program,” which involves the disassembly and recycling of discarded devices in a socially, economically, and environmentally sustainable manner. Other leading brands, such as Dell, HP, and Samsung, are also working on innovative e-waste recycling technologies and solutions to reduce the environmental impact of e-waste and maximize the reuse of valuable materials.
The exponential growth of e-waste worldwide poses a serious environmental, economic, and social challenge. Inadequate e-waste recycling leads to the waste of valuable rare and precious materials and the increasing release of hazardous materials. Innovative e-waste recycling technologies and processes are now emerging to help reduce the environmental impact of e-waste and maximize the reuse of rare and precious materials for future devices. Leading brands such as Microsoft, Apple, and Dell are developing and implementing unique e-waste recycling technologies and processes to reduce the environmental impact of e-waste and create new jobs and opportunities for local communities.
Now, the world must unite to implement innovative e-waste recycling solutions and policies that promote the maximum reuse of rare, precious, and valuable materials.
Fill out the form below to request your electronics recycling pickup.
We’ll coordinate the schedule logistics and follow up with next steps.
Before companies recycle their electronic equipment, the questions usually come quietly. They appear in internal emails, short meetings, or last-minute conversations just before a pickup is scheduled. These questions are rarely about recycling as an idea. They are about responsibility, process, and what happens once the equipment leaves the building.
At eSmart Recycling, we hear these questions every week from companies across the U.S. They come from IT managers, operations teams, and sustainability leads who want clarity before moving forward. Understanding these concerns helps companies recycle with confidence instead of hesitation.
This is often the first question companies ask, even if it is not always said out loud. Once equipment leaves the site, there is a natural loss of visibility. Companies want to know where devices go, how they are handled, and whether the process continues in a controlled way.
A structured recycling process does not end at pickup. Equipment should move through defined internal steps that are documented and traceable. When companies ask this question, they are usually seeking reassurance that recycling is not a blind handoff, but a managed sequence with clear outcomes.
Even when devices are no longer in use, concerns around data remain. Companies often ask whether equipment still contains information and how that information is addressed during recycling.
This question is less about technical detail and more about trust in the process. Companies want to avoid uncertainty once devices leave their control. Clear procedures and internal handling standards help ensure that data-related concerns are addressed early, rather than becoming unanswered questions later.
Many organizations assume that recycling starts only when a truck arrives. In reality, companies often want to know what they should do beforehand.
This includes questions about sorting, labeling, or simply understanding which devices are included. Preparation helps avoid confusion during pickup and reduces the chance of equipment being overlooked or mishandled. When companies ask this, they are usually looking for guidance rather than extra work.
Another common question is whether laptops, desktops, servers, and peripherals follow the same path once recycled. Companies recognize that not all devices are equal and want to know how differences are handled.
Clear processes account for these variations without forcing companies to manage them internally. This question often reflects a desire for simplicity paired with accountability.
As companies become more familiar with electronics recycling, they begin asking about certifications and industry standards. This question usually comes once a company has experienced unclear or inconsistent recycling in the past.
Certifications such as R2v3 are designed to bring structure and consistency to electronics recycling. R2v3 is maintained by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International and defines requirements for handling, documentation, and downstream management of equipment.
For companies, asking about certification is a way to verify that a recycler follows documented practices rather than informal methods.
Documentation is another topic that surfaces early in conversations. Companies want to know whether they will receive confirmation once recycling is complete and what that confirmation looks like.
This question is rarely about paperwork alone. It reflects a need to close the loop internally. Documentation allows teams to confirm that equipment was handled properly and that the recycling process reached a clear endpoint.
Some companies worry that recycling will interrupt daily work or require special coordination. They ask whether pickups can be scheduled smoothly and whether the process adapts to their timelines.
These questions often come from teams that have experienced rushed cleanouts or last-minute recycling efforts. Companies are looking for a process that works alongside normal operations rather than disrupting them.
Organizations often accumulate electronics over time. When they finally decide to recycle, they may have equipment from different years, departments, or uses.
Companies ask whether this creates complications. In most cases, the concern is about whether older or mixed equipment can still be handled in an orderly way. Clear intake processes help avoid confusion and keep recycling manageable, even when inventories are not perfectly organized.
Once companies begin asking questions, they often start thinking beyond the current recycling cycle. They want to know how to prevent electronics from piling up again.
This question signals a shift from reactive cleanouts to ongoing management. Companies begin to see recycling as part of regular asset lifecycle handling rather than an occasional task.
The questions companies ask before recycling are not obstacles. They are indicators of responsibility. They show that organizations want to understand what they are participating in and how their decisions carry forward.
When these questions go unanswered, recycling becomes uncertain. When they are addressed clearly, companies move forward with confidence and consistency.
At eSmart Recycling, our role is to answer these questions before they turn into concerns. We work with companies to explain each step of the recycling process in plain terms, from preparation to completion.
As an R2v3-certified recycler, we follow defined procedures that help companies maintain clarity throughout the recycling process. This allows organizations to recycle equipment knowing what happens before, during, and after pickup.
Over time, these conversations help companies shift from one-time recycling events to steady, repeatable practices.
Companies rarely hesitate to recycle because they do not care. They hesitate because they want to understand what they are handing off.
Asking questions before recycling is not a delay. It is part of responsible decision-making. With clear answers and structured processes, recycling becomes less of a concern and more of a normal operational step.
From eSmart Recycling, we see these questions as the starting point of better electronics management, not the end of the conversation.
Most companies do not mishandle old electronics on purpose. The issues usually come from habits that develop quietly over time. Equipment is replaced, stored “for later,” and gradually forgotten. What begins as a temporary solution often turns into a long-term gap in responsibility.
From eSmart Recycling, we see the same patterns across offices, schools, and organizations of all sizes. These mistakes are common, rarely intentional, and easy to overlook until they start causing operational friction.
One of the most frequent mistakes is assuming that storage equals resolution. Old desktops, laptops, servers, and networking equipment are placed in closets or storage rooms with the idea that they will be addressed eventually.
Over time, that moment never arrives. Equipment stays listed as assets without a clear plan, space fills up, and responsibility becomes diffuse. Storage does not solve anything on its own. It only postpones decisions that still need to be made.
Another common issue appears when equipment moves internally. Devices are reassigned, returned from employees, or relocated between offices. When they come back, they are often placed in storage without proper tracking.
As time passes, it becomes difficult to answer basic questions about that equipment. Accountability fades, and with it, the ability to manage those devices in a structured way. This loss of clarity usually becomes visible only when a company finally decides to clean out accumulated electronics.
Age is often mistaken for irrelevance. Many companies believe that if equipment is outdated, it no longer requires careful handling.
In practice, older devices still represent company assets and still fall under internal policies, operational standards, or reporting requirements. Treating old electronics as harmless clutter is one of the reasons companies end up with unresolved risks and repeated cleanout cycles.
When space becomes tight, some companies look for quick ways to remove equipment. Informal disposal options may seem convenient, but they often lack structure, oversight, and documentation.
Once electronics leave a company without clear records, there is no way to verify what happened afterward. From an operational standpoint, this creates gaps that cannot be closed retroactively.
Another recurring mistake is reducing electronics recycling to a single event. The objective becomes getting equipment out of the building as quickly as possible.
When removal is treated as the entire process, critical steps are overlooked. Planning, custody transfer, handling after pickup, and closure are seen as secondary. Over time, this approach leads to inconsistency and repeated corrective efforts.
Recycling works best when it is part of end-of-life asset management, not an emergency response.
Many companies stop paying attention once equipment leaves their site. This is one of the most significant blind spots in electronics management.
What happens after pickup determines whether a service is structured or superficial. Equipment should move through controlled internal processes, with clear handling and defined outcomes. Without visibility into this stage, companies are left assuming everything was handled correctly.
Standards such as R2v3, developed by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International, exist to bring structure to this part of the process.
They define how the chain of custody, downstream handling, and records should be maintained once equipment leaves the client’s control.
Documentation is often requested only when someone asks for it. Many companies recycle electronics without requiring records upfront, assuming they can retrieve them later.
In reality, documentation is most effective when it is created as part of the process itself. Pickup records, processing confirmations, and completion documentation allow companies to close the loop properly.
Without documentation, recycling remains an unresolved action rather than a completed one.
Another common pattern is handling electronics only during major cleanouts. Equipment accumulates for years and is then removed all at once.
This approach increases pressure, reduces oversight, and often forces rushed decisions. Smaller, regular recycling cycles help companies maintain control and avoid repeating the same mistakes.
Companies that correct these patterns usually start by choosing a partner that brings structure and consistency to the process. Clear standards, defined workflows, and predictable communication replace uncertainty.
As an R2v3-certified recycler, we work with organizations to manage electronics through documented steps, from planning to completion. This helps companies move away from reactive cleanouts and toward steady, controlled management of retired equipment.
Over time, recycling becomes part of normal operations instead of a recurring issue.
A common question is whether older equipment really needs the same level of attention as newer devices. Consistent handling often simplifies management and avoids exceptions.
Another question is whether past mistakes can be corrected. In most cases, they can. Bringing structure into future processes helps stabilize electronics management going forward.
Companies also ask how to avoid repeating the same issues. Regular review, clear standards, and working with qualified recyclers are usually where progress begins.
Old electronics rarely become a problem overnight. They become a problem when they are ignored.
Companies that address these common mistakes gain clarity, free up space, and reduce uncertainty. Electronics recycling shifts from a periodic scramble to a controlled, repeatable process.
From eSmart Recycling, our role is to help companies recognize these patterns early and manage retired electronics with consistency and care.
In many companies, electronics recycling starts when storage space is gone. Old equipment piles up, rooms fill quickly, and the pickup feels like the solution. What often gets overlooked is that the pickup is only a midpoint in a much longer process. In business electronics recycling, what happens before and after the pickup is what determines whether the job was handled properly or simply pushed out of sight.
From eSmart Recycling, we see that most issues do not come from the pickup itself. They come from decisions made earlier, or from a lack of structure once equipment leaves the building. Understanding the full process changes how companies manage retired technology.
Before any equipment is removed, electronics recycling is not a physical action yet. It is an operational decision. This is the moment when a company defines which devices are no longer needed and under what conditions they will leave the organization.
At this stage, equipment that is no longer in use is still part of the company’s asset landscape. Even when devices are outdated or stored away, responsibility does not disappear. Treating this phase lightly often creates confusion later, when questions arise about handling, timing, or accountability.
A serious recycling process recognizes that clarity at this point sets the tone for everything that follows.
Planning before pickup is not about adding bureaucracy. It is about control.
When companies define the scope of a pickup, the expectations for handling, and the standards the provider must follow, the rest of the process becomes predictable. When these decisions are skipped or rushed, recycling turns into a chain of assumptions.
From our experience, the most reliable recycling outcomes come from companies that treat recycling as the final stage of technology asset management, not as a last-minute cleanup.
Before pickup, coordination turns decisions into action. This is where recycling either fits smoothly into business operations or becomes a disruption.
Dates, access points, equipment types, and points of contact are established ahead of time. When this is done properly, the pickup itself is quiet and efficient. When it is not, small gaps quickly turn into operational friction.
This phase also defines a critical boundary: the moment when custody of the equipment changes. That transition should never be ambiguous. For businesses, knowing exactly when responsibility shifts is essential to closing the loop.
Pickup day is often the most visible part of electronics recycling, but it is not the end of the process. It is a handoff.
At this point, equipment leaves the company’s physical control, but operational control must continue through traceability. Devices are identified, recorded, and integrated into a chain of custody that connects the “before” to the “after.”
When pickup is treated as an endpoint rather than a transition, the rest of the process becomes disconnected. That is when uncertainty starts to grow.
Once equipment leaves the company site, recycling moves into a phase that many businesses never see, but that defines the seriousness of the service.
Devices arrive at a specialized facility where they are reviewed, sorted, and directed into appropriate processing paths. Not all equipment follows the same route, and that distinction matters. Decisions made here determine how materials are handled, how risk is managed, and how the process is documented.
This is where structure separates a controlled service from an informal one.
In the United States, the R2v3 (Responsible Recycling) standard, developed by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International, exists to bring order to what happens after pickup.
R2v3 defines requirements for the chain of custody, downstream controls, material handling, and documentation. It is not only about recycling outcomes, but about maintaining responsibility throughout the entire lifecycle of retired equipment.
As an R2v3-certified company, we work within this framework because it prevents the process from becoming opaque once equipment leaves the client’s site.
After pickup, devices that may contain data follow defined internal procedures. This stage is critical, not because it is dramatic, but because it removes uncertainty.
When data handling is treated as an integrated part of recycling, it does not become a separate concern later. When it is treated as an afterthought, questions remain long after the equipment is gone.
For many businesses, this is where the difference between a basic service and a serious partner becomes clear.
Once equipment has gone through the necessary processing stages, materials are managed according to their characteristics. Metals, plastics, and electronic components move through different controlled paths.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency encourages businesses to work with qualified electronics recyclers to ensure responsible material management and oversight.
This approach reduces the risk of unclear downstream practices and reinforces accountability beyond the initial pickup.
The final stage of electronics recycling is often the one that companies appreciate most over time. Documentation closes the process.
Records of pickup, processing, and completion allow businesses to look back and confirm that equipment was handled properly. These records support internal reviews, sustainability reporting, and operational clarity.
From our perspective, documentation is not an optional add-on. It is how recycling becomes a closed process instead of an open question.
Companies that understand what happens before and after pickup do not recycle out of urgency. They recycle with intent. They know what to expect, what to require, and how to evaluate the service they receive.
For the organizations we work with, electronics recycling becomes part of structured asset management rather than a recurring operational headache.
Electronics recycling for businesses does not begin when a truck arrives, and it does not end when equipment leaves the site. It begins with informed decisions and ends with documented outcomes.
From eSmart Recycling, we support companies throughout that entire path, before and after pickup, because that is where responsible electronics recycling is truly defined.
When a company looks for a technology recycling service, it is not just trying to get rid of old equipment. It is looking for certainty. Certainty about data, responsibility, and what actually happens to those assets once they leave the building.
From eSmart Recycling, this is a conversation we have constantly with businesses in Tampa and across the U.S. Many companies already recycle, but not all of them know what a serious service should truly include. That is why it helps to lay it out clearly, based on daily work, not marketing language.
For us, a solid technology recycling service does not begin when a truck arrives. It begins when a company decides that equipment is no longer needed and wants clarity about the full process.
A serious provider should be able to explain what happens before, during, and after pickup. There should be no vague answers and no missing steps. Businesses need to know exactly when responsibility transfers and how that moment is documented.
If that explanation is not clear from the start, the service already has a weak point.
One of the first things we look at when defining a serious service is certification. In the U.S., R2v3 (Responsible Recycling), developed by Sustainable Electronics Recycling International (SERI), sets clear requirements for handling electronic equipment in business environments.
R2v3 defines how the chain of custody is managed, how downstream vendors are controlled, and how records are maintained. For us, this certification structures the entire service. It is not about checking a box, but about operating within a system that can be reviewed and verified.
A service that cannot demonstrate this level of structure leaves too many open questions for a business.
Data is often underestimated, especially when equipment has been stored for a long time. Many devices still contain storage media even after years of inactivity.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) addresses this in NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 1, which outlines accepted methods for data sanitization before disposal or recycling.
A serious technology recycling service does not treat data as an afterthought. From our perspective, devices with potential data are identified and handled from the first conversation, using defined and traceable processes.
A proper recycling service should make things easier for the company, not harder. Businesses should not have to manage transportation, disassembly, or complex coordination.
From our side, logistics are designed to fit into normal business operations. We coordinate pickup, record the equipment, and manage transportation without turning internal teams into project managers for recycling.
If a service adds friction, it usually means the process is not designed for business use.
Documentation is often only appreciated when it is needed. Audits, sustainability reports, and internal reviews are when companies realize how important records are.
A serious service includes documentation as a standard step. Records of what was collected, when it left the site, and how it was managed afterward are essential to closing the loop properly.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) encourages businesses to work with qualified electronics recyclers as part of responsible materials management.
That guidance aligns closely with the need for traceability and clear records.
Not all recycling services are designed for companies. Some focus mainly on residential drop-offs or one-time events. Those models do not always translate well to corporate environments.
Working with businesses requires understanding internal approvals, IT refresh cycles, storage cleanouts, and administrative requirements. From our experience, knowing how companies operate is just as important as knowing how to process equipment.
A serious service adapts to business realities instead of expecting businesses to adapt to it.
It is common to see informal recycling offers that promise quick removal with little structure. These options may seem convenient, but they leave too many gaps.
Once equipment leaves a company without documentation or clear oversight, accountability is gone. From our perspective, structured processes exist to prevent exactly that situation.
A serious service prioritizes clarity and control over speed alone.
When companies work with us, they receive a service built around R2v3 certification, defined workflows, coordinated logistics, and clear documentation. Our goal is to turn technology recycling into a closed process, not an ongoing concern.
We do not offer shortcuts. We offer structure, traceability, and consistency.
For many businesses, that is what allows them to move forward without uncertainty.
Companies often ask whether all equipment needs the same treatment. It does not. A serious service explains those differences clearly.
Another frequent question is whether certification truly matters. From our experience, it defines how the entire service operates.
There is also the question of switching providers. In most cases, choosing the right service simplifies future recycling efforts instead of complicating them.
The technology recycling service a company chooses reflects how it manages end-of-life assets. That choice becomes part of internal operations, whether it is visible or not.
For companies that value order and accountability, working with eSmart Recycling means operating under clear standards, documented processes, and predictable outcomes. From our side, that is the commitment we bring to every service.
Choosing an electronics recycling company in Tampa is not just a vendor decision. It is a responsible decision. From our side at eSmart Recycling, we see this question every week from companies that want to do things properly but are not sure what really matters when comparing options.
So instead of listing promises, we prefer to explain how we look at this decision ourselves, because that is exactly how we work with our partners.
When companies call us, the first thing we clarify is responsibility. For us, recycling electronics is not about pickup day. It starts the moment the equipment is taken out of use.
As eSmart Recycling, we are very clear about when responsibility transfers from the company to us and how that moment is documented. We believe businesses should never wonder who is accountable once equipment leaves their facilities.
If a recycler cannot explain that clearly, we usually see problems later. And those problems never stay with the recycler; they stay with the company.
One of the main reasons companies choose us is our R2v3 certification, developed by SERI (Sustainable Electronics Recycling International).
We do not see R2v3 as a badge. We see it as a framework that defines how we operate every day. Chain of custody, data handling, downstream processing, and recordkeeping are part of our normal workflow, not optional steps.
When we work with businesses, that certification gives structure to the entire process. It also gives our partners something concrete to rely on, especially when audits or internal reviews come up.
From our experience, data concerns are often underestimated. We regularly see equipment that has been stored for years and still contains storage devices.
We follow guidance such as NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 1, published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), which outlines accepted data sanitization methods.
https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-88/rev-1/final
When companies work with eSmart Recycling, data handling is addressed from the start. We do not wait until the equipment arrives at our facility to ask questions. We plan for it before pickup happens.
We design pickup around how businesses actually operate. Our goal is not to create extra work for IT teams, facilities managers, or sustainability leads.
As eSmart Recycling, we coordinate pickup directly at the company location, log the equipment, and handle transportation ourselves. Companies should not need to solve logistics problems to recycle electronics responsibly.
From our point of view, if recycling creates friction, something is wrong with the process.
We treat documentation as part of responsible operations, not as an add-on. Every pickup we handle includes records that show what was collected, when it left the site, and how it was processed.
Many of the companies we work with only realize the value of this documentation months later, during audits, sustainability reporting, or internal reviews. Our role is to make sure those records exist before anyone needs to ask for them.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) encourages businesses to work with qualified electronics recyclers as part of responsible materials management.
That guidance aligns closely with how we structure our services.
We work mainly with business clients. Offices, schools, healthcare organizations, and companies are going through IT refresh cycles or relocations.
That experience shapes how we communicate, how we schedule, and how we manage expectations. Business recycling is different from residential drop-offs or one-time events, and we treat it that way.
For us, understanding how companies operate is just as important as understanding the equipment itself.
We often speak with companies that considered informal or undocumented recycling options before contacting us. Those options usually sound simple, but they leave too many unanswered questions.
Once equipment leaves a company without clear oversight, accountability is gone. As eSmart Recycling, we believe structured processes exist to prevent exactly that situation.
Companies that choose to work with us usually do so because they want clarity. They want to know who is responsible, how the equipment is handled, and what records remain afterward.
We operate under R2v3 certification, manage pickup and processing through defined workflows, and communicate openly throughout the process. That is how we reduce uncertainty for the businesses we work with.
For many of our partners, that clarity is what turns electronics recycling into a resolved task instead of a recurring concern.
We are often asked whether certification really makes a difference. From our perspective, it defines how a recycler operates.
We are also asked whether all equipment is treated the same way. It is not, and part of our job is explaining those differences clearly so companies know what to expect.
Another common question is whether changing recyclers is complicated. In our experience, choosing the right partner early makes everything easier later.
The electronics recycling company you choose reflects how your company handles responsibility. That choice tends to stay with you longer than expected.
For businesses in Tampa, working with eSmart Recycling means working with a team that takes responsibility seriously, follows recognized standards, and keeps the process clear from start to finish.
From our side, the goal is simple: help companies recycle electronics with confidence and without loose ends.
If your company has old PC towers that have been sitting in storage for years, you are not alone. Many offices end up with stacks of desktop towers kept after upgrades, moves, or changes in IT strategy. They are rarely used again, yet they keep taking up space and quietly carry responsibility with them.
So, what should a business actually do with PC towers that have been stored for years? The short answer is to remove them through a certified, documented recycling process. The longer answer explains why waiting rarely helps and how to handle them properly.
Desktop towers often survive several technology cycles. Laptops replace them, cloud services reduce on-site hardware, and offices shrink or relocate. Yet the towers remain.
They are stored “just in case.” In case someone needs spare parts. In case a system must be rebuilt. In case data is still needed. Over time, those reasons fade, but the equipment stays.
What many companies overlook is that keeping old towers does not make the situation safer or simpler. It only postpones a decision that eventually has to be made.
Even if a PC tower has not been powered on for years, it may still contain hard drives, solid-state drives, or other storage media. Those components can hold files, credentials, system configurations, or personal data.
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) addresses this issue in its data sanitization guidance. NIST SP 800-88 Rev. 1 explains that storage media must be properly sanitized before disposal or recycling to reduce data exposure risks.
https://csrc.nist.gov/publications/detail/sp/800-88/rev-1/final
From a business standpoint, the age of the equipment does not eliminate responsibility. Data does not disappear on its own.
PC towers are electronic waste. They contain metals, plastics, circuit boards, and components that require proper handling. Disposing of them through regular trash or informal channels is not recommended for businesses.
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) encourages companies to recycle electronics through qualified recyclers to ensure responsible material management and reduce environmental risk.
For organizations with sustainability reporting, internal audits, or compliance requirements, improper disposal creates gaps that are difficult to justify later.
There is a point where storage stops being a safety net and becomes a liability. Towers take physical space, create clutter, and require tracking, even if no one touches them.
From an operational perspective, if a PC tower has not been used in years and has no defined future purpose, keeping it rarely adds value. Recycling it through a documented process closes the loop and removes uncertainty.
This is often the moment when companies decide to act.
A proper process starts by identifying which towers are no longer needed. This includes confirming whether they contain storage devices and whether those devices require certified data sanitization or physical destruction.
The equipment is then collected through a controlled pickup process and transported to a certified facility. There, devices are audited, storage media are handled according to accepted standards, and materials are processed responsibly.
Documentation is a key part of this process. Many businesses need records that show when equipment left their control and how it was managed afterward.
In the U.S., one of the most recognized standards for responsible electronics recycling is R2v3 (Responsible Recycling), developed by SERI (Sustainable Electronics Recycling International).
R2v3 certification sets requirements for the chain of custody, data handling, downstream processing, and recordkeeping. It applies whether the equipment was used yesterday or stored for a decade.
At eSmart Recycling, we operate under R2v3 certification. For companies, this means old PC towers are handled through a structured, documented process designed for business environments.
When businesses contact us about PC towers that have been stored for years, the first step is clarity. We review what equipment needs to be removed and what type of storage may be involved.
We coordinate pickup directly from the company location, log the equipment, and transfer it to our facility for proper processing. From that point forward, responsibility for those towers is clearly defined.
This clarity is especially important for IT teams, facilities managers, and sustainability leads who want to resolve long-standing storage issues without creating new ones.
While there is no single federal law focused only on PC towers, broader guidance applies. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) emphasizes the responsibility of businesses to dispose of electronics containing sensitive information securely.
https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/resources/disposal-rule-facts-businesses
For regulated industries, proper disposal supports internal policies and reduces exposure during audits or reviews.
A frequent question is whether towers that no longer work still need special handling. The answer is yes. Functionality does not determine whether data is present or whether components require responsible recycling.
Companies also ask if towers can be recycled together with other electronics. In most cases, they can. Certified recyclers are equipped to manage mixed loads safely.
Another question is whether the process will disrupt operations. When coordinated properly, pickup and recycling can be scheduled with minimal impact.
The longer PC towers sit in storage, the easier they are to forget and the harder they are to explain later. Acting now removes clutter, reduces uncertainty, and simplifies recordkeeping.
According to the EPA, working with qualified electronics recyclers supports better management of retired equipment and helps businesses maintain orderly operations.
Recycling old PC towers is not about rushing. It is about closing a chapter that has been open for too long.
For companies, the best answer to years of stored PC towers is a clear, documented recycling process. Certification, experience, and transparency matter more than convenience alone.
With the right partner, dealing with old PC towers becomes a straightforward task rather than a lingering question.






Did you enjoy our latest blog articles just above?
Subscribe to receive new stories, insights, and impact updates straight to your inbox.
We’ll send you curated content about our partners, recycling strategies, success stories, and how your involvement is driving change through technology access and digital empowerment.
💡 No spam, just the smart stuff.